




Cell biology
99 Dictionaries: The world of terms
Cell biology의 설명
큰 과학 백과 사전 "세포 생물학" - 감수 분열 및 유사 분열, 사이토 카인, 세포 과정, 신호 전달, 운동, 성장 인자 등
세포 생물학(또한 세포 생물학 또는 세포학) - 세포 과학. 세포학의 주제는 생명의 구조적 및 기능적 단위로서의 세포입니다. 세포학의 임무에는 세포의 구조와 기능, 화학적 구성, 개별 세포 구성 요소의 기능, 세포 재생산 과정, 환경 조건에 대한 적응, 특수 세포의 구조적 특징 연구 등이 포함됩니다. 세포 생물학 연구 유전학, 분자 유전학, 생화학, 분자 생물학, 의료 미생물학, 면역학 및 세포 화학과 같은 다른 분야와 상호 연결되어 있습니다.
소기관은 구조가 다르고 다양한 기능을 수행하는 영구적인 세포내 구조입니다. 소기관은 막(2막과 1막)과 비막으로 세분됩니다. 2막 구성 요소는 색소체, 미토콘드리아 및 세포핵입니다. 액포 시스템의 소기관은 소포체, 골지 복합체, 리소좀, 식물 및 곰팡이 세포의 액포, 박동 액포 등의 단일 막 소기관입니다. 비막 소기관에는 리보솜과 세포 중심이 포함되며 이는 셀.
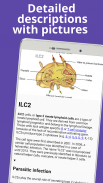
미토콘드리아는 모든 진핵 세포의 필수적인 구성 요소입니다. 그것들은 세분화되거나 실 모양의 구조입니다. 미토콘드리아는 외부와 내부의 두 막으로 둘러싸여 있습니다. 외부 미토콘드리아 막은 그것을 hyaloplasm과 분리합니다. 내막은 미토콘드리아 내에서 소위 크리스태(cristae)라고 불리는 많은 함입을 형성합니다.
유사분열은 유전 물질(염색체)이 새로운(딸) 세포 사이에 균등하게 분포되는 세포 분열 방법입니다. 코어를 두 개의 자식으로 나누는 것으로 시작합니다. 세포질도 마찬가지로 나누어집니다. 한 분열에서 다른 분열로 일어나는 과정을 유사분열 주기라고 합니다.
감수 분열은 생식 세포 형성의 한 단계입니다. 원래 이배체 세포(염색체 2세트 포함)의 연속적인 2개 분열과 4개의 반수체 생식 세포 또는 배우자(염색체 1세트 포함) 형성으로 구성됩니다.
필라멘트 단백질 구조의 집합인 세포골격 - 세포의 근골격계를 구성하는 미세소관 및 미세섬유. 세포골격은 진핵 세포만이 소유하고 있습니다. 원핵 생물 (박테리아)의 세포에는 없습니다. 세포골격은 단단한 세포벽이 없는 경우에도 세포에 일정한 모양을 부여합니다. 그것은 세포질에서 소기관의 움직임을 조직합니다. 세포골격은 쉽게 재배열되어 필요한 경우 세포 모양의 변화를 제공합니다.
아미노산은 단백질의 구조적 구성 요소입니다. 단백질은 생물학적 헤테로폴리머이며, 그 모노머는 아미노산입니다. 약 200개의 아미노산이 살아있는 유기체에서 발견되는 것으로 알려져 있지만 그 중 20개만이 단백질의 일부입니다. 이들은 염기성 또는 단백질 형성(단백질 생성) 아미노산입니다.
화학적 성질에 따라 효소는 단순하거나 복잡한 단백질입니다. 그들의 분자에는 비단백질 부분인 코엔자임이 포함될 수 있습니다. 효소의 작용 메커니즘은 촉매 반응의 활성화 에너지를 줄이는 것입니다. 이것은 반응 물질에 효소를 부착하고 그들과 중간 복합체를 형성함으로써 달성되며, 그 결과 반응의 에너지 역치가 감소하고 원하는 방향으로 진행될 확률이 급격히 증가합니다.
이 과학 사전 세포 생물학 책은 오프라인에서 무료로 제공됩니다.
• 특성 및 용어에 대한 7500개 이상의 정의가 포함되어 있습니다.
• 전문가, 학생 및 애호가 모두에게 이상적입니다.
• 자동 완성 기능이 있는 고급 검색 기능 - 입력하는 대로 검색이 시작되고 단어를 예측합니다.
• 음성 검색;
• 오프라인 작업 - 앱과 함께 패키지된 데이터베이스, 검색 시 발생하는 데이터 비용 없음;
• 생물학을 배우기 위한 책이나 빠른 참조를 위한 이상적인 앱입니다.


























